Overview
Knee pain when bending the knee is a common problem of knee joint, more likely to occur in aged individuals.
The knee joint is the largest joint of the body. Therefore, it has to sustain the greatest stresses since it supports the entire weight of the body above it.
This joint mainly allows for flexion and extension. This flexion movement is known as knee bending.
In daily life, we have to bend our knees so many times. For example, to walk, climb stairs, wear clothes, and even sleep. Also, exercise, this joint has a huge role to play.
The knee joint is designed to do all of these. But sometimes, it hurts whenever we have to bend our knees.
The pain of the knee joint, particularly when bending the knee, can be explained in several ways. First, the cause of the pain has to be evaluated and treated.
This article discussed the cause, symptoms analysis, remedies, and treatment of knee peen when bending the knee in detail.
Basic Anatomy of knee joint
Learning the basic anatomy of the knee joint will help you understand the cause of your pain. In addition, you can now relate to the image and understand it way better.
The knee is one of the body’s largest and most complex joints. The knee joins the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone). The smaller bone that runs alongside the tibia (fibula) and the patella (kneecap) is the other bones that make the knee joint.
Tendons connect the knee bones to the leg muscles that move the knee joint. Ligaments join the knee bones and provide sufficient stability to the knee.
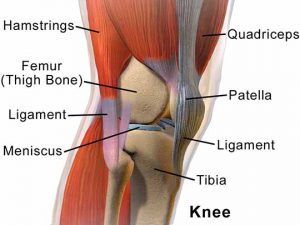
- The anterior cruciate ligament prevents the femur from sliding backward on the tibia (or the tibia sliding forward on the femur).
- The posterior cruciate ligament prevents the femur from sliding forward on the tibia (or the tibia from sliding backward on the femur).
- The medial and lateral collateral ligaments prevent the femur from sliding side to side.
- Two C-shaped cartilage named the medial and lateral menisci act as shock absorbers between the femur and tibia.
Read Rhizotomy
Read Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS)
Knee Pain When Bending Causes
There are so many causes of knee pain while bending. But here are some most common causes;
Patellar Tendonitis
Patellar tendonitis is one of the principal causes of pain behind the knee when bending. It’s also known as Jumper’s knee. It is a condition characterized by inflammation of the patellar tendon. The patellar tendon connects the patella (kneecap) to the tibia(shin bone).
Patellar tendonitis weakens your tendon and, if untreated, can lead to tears in your tendon.
Signs of Patellar Tendonitis
Burning pain and tenderness around your patellar tendon (base of your knee cap). Swelling. Pain with jumping, running or walking.
Patellofemoral Syndrome
Patellofemoral pain syndrome is pain at the front of your knee, around your patella (kneecap). It’s also called Runner’s knee.
The patellofemoral syndrome may lead to pain when bending the knee.
People who participate in sports that involve running and jumping suffer most from it.
The knee pain often increases when you run, walk up or downstairs, sit for long periods, or squat.
Sign & Symptoms
Dull, aching pain in the front of your knee. What Can be exaggerated with;
- Climbing the stairs
- Squat or Kneel position
- Sit with a bent knee for a long period of time.
Hamstring Tendonitis
Hamstring tendonitis occurs when the soft tissues that connect the muscles of the back thigh to the pelvis, knee, and lower legs become inflamed.
Hamstring Tendonitis is often brought on by overuse of the knee joint. And it causes knee pain when bending and straightening and often decreases with rest.
Sign & Symptoms
- Mainly pain behind your knee and thigh.
- Sharp, burning pain
- Muscle and joint weakness
- Aching or dull throbbing
- Muscle and joint stiffness
- Swelling or inflammation
Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS or IT band syndrome) is an overuse injury of the connective tissues located on the outer part of the thigh and knee.
It causes pain and tenderness in the outer area of the thigh and knee, especially just above the knee joint.
The doctor may advise you following investigations for evaluating Iliotibial Band Syndrome;
- Renne’s Test
- Noble’s Test
- Ober’s Test
Quadriceps Tendonitis
The quadriceps tendon is located just above the Patella (Kneecap) and connects the quadriceps muscles in the front of the thigh to the top of the patella (kneecap).
The function of the quadriceps tendon is to work with the patellar tendon along with the muscles in the front of the thigh to straighten the knee.
Therefore, both tendons are instrumental in allowing people to perform activities such as climbing stairs, walking, running, and jumping.
Tendonitis is a common overuse injury caused by repeated and prolonged stress on a tendon. This repeated stress (micro-trauma) on the tendon can lead to the tendon becoming thickened and tiny tears developing in the tendon.
The body attempts to repair these tiny tears, but if the rate of breakdown within the tendon exceeds the rate of repair, this can lead to pain and dysfunction.
- Pain: The pain occurs in the anterior knee above the kneecap. The pain is often worse with activities such as running, jumping, walking up and downstairs, and squatting, and it can also occur with prolonged sitting with a bent knee.
- Stiffness: The tendon can often feel stiff, mostly in the morning or after exercise and physical activity.
- Swelling: The painful tendon may appear thickened or swollen compared to the non-affected tendon.
Knee Bursitis
Knee bursitis (prepatellar or infrapatellar bursitis and housemaid’s knee) occurs when fluid-filled sacs known as bursae become damaged, irritated, or inflamed.
Normally, bursae (fluid-filled sacs) act as a cushion or friction-reducer between 2 body parts, such as bone and skin, bone and ligament or tendon.
Bursae on the front of the knee serve as cushions between the patella and skin and between the patellar tendon and tibia bone.
Prolonged pressure or traumatic blows can injure a bursa. And repetitive overuse can cause irritating friction on it, leading to the development of bursitis. “itis” means “inflammation.”
When the bursa is injured, it can swell and become extremely painful.
- Swelling on the front of the kneecap.
- Visible redness on the front of the knee.
- Pain when you put pressure with your fingers on the front of the knee.
- Pain when kneeling or squatting.
- Stiffness in the knee joint and difficulty when extending or bending the knee.
Complicated Causes
There are some complicated knee conditions, which can also cause pain in the knee while bending. Let’s discuss those.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative bone disease that worsens over time, often resulting in chronic pain. Joint pain and stiffness can become severe enough to make someone’s daily life very difficult.
Depression and sleep disturbances can result from the pain and disability of osteoarthritis. In addition, someone can be physically immobile because of this disease.
Sign and symptoms
- Severe Pain.
- Noticeable Joint Stiffness.
- Tenderness while puts pressure on this joint.
- Loss of flexibility.
- Grating sensation when you use the joint for movement.
- Bone spurs.
- Swelling around the joint.
Baker’s Cyst
A Baker’s cyst is a fluid-filled cyst that causes a visible bulge and a feeling of tightness behind your knee joint. The pain can get worse when you fully straighten or bend your knee or when you’re active.
Sign and symptoms
- Swelling behind your knee joint and sometimes in your leg also.
- Severe Knee pain.
- Stiffness and feeling pain to fully bend the knee.
Any injury or trauma to the knee joint or its ligaments or attached muscle may cause severe pain, swelling, and inability to move the knee.
You may be puzzled by so much information. With so many diseases, signs and symptoms, it’s hard to determine your very own problem. So here we’re making it easier for you.
Separating those diseases and conditions according to the site of your knee joint and sign and symptom.
Now you can scroll to the sign and symptoms that match you and read out the possible causes.
Pain behind your knee pain when bent
The pain behind your knee is possible because of;
- Hamstring tendonitis
- Baker’s cyst
- Knee injury or trauma
Very sharp pain in your knee when you are bending
The sharp pain in your knee is possibly because of;
- Torn one or more ligament
- Any fracture in the knee or patella
- Degenerative diseases such as osteoarthritis
- Patellar (knee cap) tendonitis
Pain above the patella (kneecap) when you are bending
If you hurt above your knee when you are bending, possibly because of;
- Quadriceps tendonitis(“itis” means irritation)
- Degenerative diseases such as;
- Osteoarthritis
- Knee bursitis (housemaid’s knee)
Pain exactly in front of your kneecap(patella) when you are bending
Pain in the front of your patella (kneecap) possibly due to;
- Patellofemoral syndrome
- Patellar tendonitis & quadriceps tendonitis
- Knee bursitis
- Fracture in patella
Home Remedy
If you are experiencing mild to moderate pain when bending the knee, you may follow the following remedies to get some relief.
Rice method
RICE method is a classic first aid method.
Most of us read this in high school biology and biological studies. As soon as possible after an injury, such as a knee, ankle, shoulder, or any bone injury, you can relieve pain and swelling and promote healing with RICE.
Rice is an acronym for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
Rest: Rest and protect the injured or painful knee area. Take a break from any activity that may be causing pain or soreness in the knee. Don’t put any weight in the sore area.
Ice: Cold will reduce pain and swelling. You may have seen applying cool spray on an athlete’s injury or sore area. Apply an ice or cold pack right away to prevent or minimize swelling and pain.
Apply the ice or cold pack for 10 to 20 minutes straight, three or more times a day. If swelling is gone after 48 to 72 hours, don’t forget to apply heat to the area that hurts.
Do not apply ice or heat directly to the skin; it will worsen the situation. Instead, place a towel over the cold or heat pack before applying it.
Compression or wrapping the injured knee area with a bandage will help decrease swelling and pain. Don’t wrap it too tightly because this can cause more swelling below the affected area. Make sure to Loosen the bandage if it gets too tight.
Signs that the bandage is too tight include numbness, tingling, increased pain, coolness, or swelling in the area below the bandage. Talk to a doctor or physician if you think you need to use a wrap for longer than 48 to 72 hours. Again, always make sure that the bandage is not too tight or loose.
Elevation: Elevate the injured or sore area on pillows while applying ice. And anytime you are sitting or lying down. Try to keep the leg at or above the level of your heart to help minimize swelling and pain.
Minimize daily physical activity
Pay close attention to your knee condition before any activities. If you feel pain during any activity, avoid it as soon as possible. And try to avoid it until you get cured.
Try to minimize any heavy work. Knee support our full body. Therefore, any heavy work affects the knee. So, keep this in mind.
You can do certain activities which may help you to improve your condition: such as;
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Yoga
- Walking
Heat
If you feel stiffness on your knee, you may apply moderate heat to it. As heat increases circulation, it helps to reduce the stiffness and offer more relief.
Massage
Massage helps to reduce the tension and stiffness of the muscle, tendon, and ligaments. For example, suppose you are an athlete or got injured during a sports activity. Then consider the sports massage. It’s specially designed for athletic persons.
The following massages can be useful;
- Remedial massage
- Swedish massage
- Deep tissue massage
Over The Counter Medication
We suggest you not take any medication without consulting a doctor. But still here suggesting some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID); you don’t need any prescription to buy them.
These medicines may also help relieve your pain and swelling.
- Ibuprofen, such as Advil or Motrin.
- Naproxen, such as Aleve or Naprosyn
- Paracetamol
Be safe with medicines. Read and follow the instruction on the label.
Exercise and Yoga
- Try to focus on the exercise of those muscles which support the knee. The knee will be less stressed when these muscles are healthy and strong.
- It’s also important to focus on Yoga. Yoga makes you flexible. The more flexible you are, the less stress you will feel on the knee joint. Try to stretch your knee by following a stretching routine.
- Make sure you are moving slowly with that routine. Please don’t rush into multiple exercises on the first day; it’ll worsen the situation.
Knee Pain When Bending Treatment
Physiotherapy
The physiotherapist will introduce you to some exercises and help you do them, improving your knee’s strength, mobility, and flexibility.
Orthotics
orthotic shoe inserts help to stabilize the feet and correct poor foot function. Orthotics can be used to prevent the unnatural rotation of the lower leg, thereby treating the cause of the specific type of knee pain.
By supporting the arches, they force the ankles and legs back into alignment, reducing the twisting on the knee and thereby providing relief to the painful knee joint.
Restrict mobilization
If your knee pain is due to an injury to the bone, muscle, or ligaments, a doctor might have you wear a brace. It will protect your knee and prevent you from moving it, helping reduce the pain and allow faster healing.
Surgical Treatment
If the condition doesn’t improve with non-surgical treatments, the doctor might tell you that you need surgery. Don’t be panicked. Surgery is only needed when there is no other way. There are so many surgeries for knee pain when bending issues; doctors mostly suggest;
ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) reconstruction
ACL reconstruction is surgery to replace a torn anterior cruciate ligament (a major ligament in your knee joint). ACL injuries most commonly occur during sports involving sudden stops and direction changes, such as basketball, football, downhill skiing, and gymnastics.
In this surgery, the torn ligament is removed and replaced with a piece of tendon from another part of your knee or a donor. This surgery is an outpatient procedure performed through small incisions around your knee joint.
ACL reconstruction is performed by a doctor(orthopedic surgeon).
Total knee replacement
A total knee replacement is a surgical procedure where the diseased knee joint is replaced with artificial material. The knee is a hinge type of synovial joint that provides motion at the point where the thigh meets the lower leg.
The femur(thighbone) touches the large bone of the lower leg (tibia) at the knee joint.
Tibial Tubercle Transfer
Tibial tubercle transfer also known as osteotomy or bony realignment, is a surgical treatment option for instability, arthritis, or cartilage defects affecting the patellofemoral joint (kneecap and femur).
During the operation, the orthopedic surgeon moves a small portion of bone where the patella tendon and repositions or transfers it to a location on the tibia (shinbone) in order to correct the underlying problem.
When to See a Doctor?
You may not need to consult a doctor as soon as you feel knee pain when bending and straightening.
You may experience certain conditions when you need to see a doctor.
Severe(extreme) knee pain
- Inability to extend or flexing your knee
- Swelling and redness around or in your knee
- Knee weakness (sometimes it’s even hard to stand)
- Popping sound when extending or flexing your knee along with pain.
- Fever and difficulty sleeping and daily activities.
If you can relate to any of the above signs, don’t consult a doctor and undergo suggested treatment.
Knee Pain When Bending Diagnosis
You may be wondering what other than an X-ray can be used to diagnose knee pain.
But you better know that an x-ray is not the only way to diagnose your cause of pain. There are several investigations to diagnose the cause properly. Here are some;
- Physical exam: doctor tries to find out the underlying cause by checking you physically.
- X-ray and MRI
- Several blood tests
So, please consult with a doctor and follow a doctor’s instructions.
Recovery
Usually, it takes 6-8 weeks to recover fully from a knee injury.
But if you undergo surgery, then it may take eight weeks to 12 months. It’s an approximate value; there are many factors, such as;
- The severity of your pain and injury condition
- Type of surgery or injury and how critical it is
- Your overall health conditions
- Your strength and activity level prior to surgery
- Your age
- Your treatment plans
- Your daily activities and diet plan
It takes some time to recover from a knee injury; keep patience and follow the doctor’s instructions.
Prevention
Nobody in the world wants an injury, but still, it happens. But here are some tips you may follow to avoid getting injured.
- Avoid the movements that cause pain in the knee. Don’t overuse the knee joint. Stay focused while doing exercise; it’ll help you prevent certain injuries.
- Improve your daily lifestyle. Try to do some basic exercise like cycling, swimming, etc. It will strengthen your muscle, tendons, and ligament.
- Lose weight if you’re overweight. Extra weight can stress your knee because the knee has to support the whole body.
- Warm up and take a little break (minimum 1 minute) before each exercise. It will protect your muscles and help prevent injury.
- Add weight training to your workout routine. Focus on strengthening the muscles that support your knee joint.
- Do Yoga regularly to loosen tight muscles and improve flexibility.
- You can use knee pads while working on your knees. Knee pads will protect your kneecaps(patella) and reduce pressure.
Takeaway
Knee pain when bending the knee is a common problem and can be treated with conservative treatment without surgery.
Sometimes other complications are associated with knee pain that must be corrected and take some time.
If you are experiencing pain when bending your knee, you may consult a doctor and get treated.
Last Updated on October 18, 2022 by Learn From Doctor Team