Table of Contents
Bruise on Eyelids Overview
A flat, blue, or purple patch measuring 1 centimeter (cm) or more in diameter is defined by the term ecchymosis(bruise on eyelids).
While this is rather confusing, the name is sometimes used synonymously with purpura or bruising.
Ecchymosis happens when blood spills under the skin from a damaged capillary into the surrounding tissue. It produces discoloration.
The region of ecchymosis may change from purplish or blackish blue to yellow or green as the tissue heals. Typically, ecchymosis can take between 1 and 3 weeks to overcome.
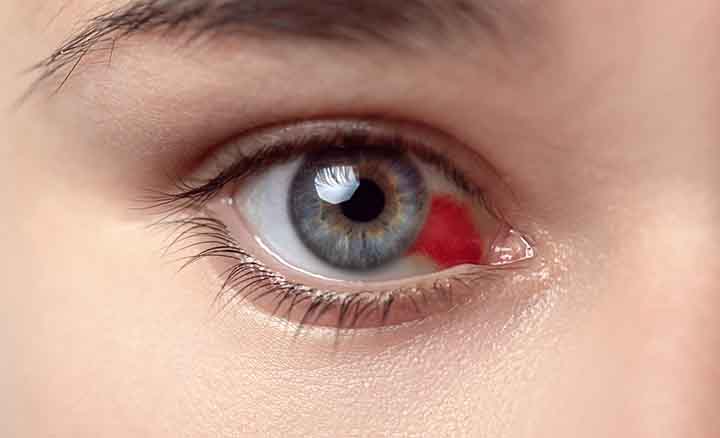
Symptoms of Bruise on Eyelids
Decolored skin is the key symptom of ecchymosis, caused by the bursting of the capillaries and blood leakage under the skin. The color of the patch is consistent with how old and serious the injury is.
The region of ecchymosis may appear dark blue, black, or purple if the leakage is recent, but over time it will fade to yellow or green.
Usually, ecchymosis alone is not a cause for concern. It is most common on legs and arms, including bruises, and it also results from minor injuries caused by bumping into furniture, for example. Ecchymosis often occurs commonly in places where the skin, such as the eyelids or lips, is small.
In highly active children and in older adults, it is normal to see ecchymosis and bruising because the skin thins and capillary walls become more porous with age.
In individuals of any age, if trauma is not responsible for ecchymosis, it may occur.
Read Red Veins on Eyelids
Causes of Bruise on Eyelids
Blood vessels may be ruptured or damaged by a fall, hit, or bump into a hard object. Blood vessels that are ruptured allow blood to collect, resulting in ecchymosis.
These injuries also lead to bruising as well. Ecchymosis is different from bruising since causes other than injury can contribute to it. They include:
- Anticoagulants, such as warfarin and aspirin,
- varicose veins
- Surgical Procedure
- Abnormalities of platelets, such as a low platelet count
- Fractures and bones
- Kidney end-stage condition
- Hemophilia and other disorders of bleeding
- Leukemia
- Dengue fever
Treatment Procedure of Bruise on Eyelids
If no clear cause of ecchymosis occurs, consult a doctor.
Patches with ecchymosis can go away without medication most of the time. By using a cold compress or over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen, a person may relieve any pain or swelling.
If a person has not had an injury and the cause of ecchymosis is not clear, certain diagnostic tests can be done by a doctor. They can prescribe an X-ray or MRI scan, depending on the severity of the bruising.
To check a person’s platelet count and clotting factors, a doctor can also examine the area and take blood.
For the development of a treatment plan, identifying the underlying cause of ecchymosis is important.
When to consult a doctor
Ultimately, any amount of inner bleeding can be indicated by ecchymosis. It should not be disregarded if serious.
Sometimes, mild bleeding is not a cause of concern. Talk to a doctor, however, if the cause is unknown, if discoloration continues over time, or if ecchymosis also occurs.
You may still didn’t understand that “do you have bruises on the eyelid or injury on the eyelid. So, to make it easy for you and more understandable, We are discussing that too.”
Injury on eyelids
At any time and in any location, an eye injury can happen. During sports and leisure events, an estimated 50 percent of accidents occur, more frequently in children and teenagers than in any other age group.
Several toys and popular household products, such as soccer balls, tennis balls, baseballs, pencils, markers, darts, knives, fishing hooks, scissors, paintball weapons, pellet guns, BB guns, forks, hangers, rubber bands, or kitchen gadgets, can trigger eye injuries. Chemicals used in the home can also cause the eye to experience serious injury. This includes bleach, cleaning products, detergent pods for the dishwasher, and even some soap.
Many different structures, including the eyelids, the bones that support the eye, and/or the eyeball itself, may be affected by eye trauma. Blunt trauma, sharp penetrating trauma, or chemical trauma can be traumatic. Anything like a ball or fist that hits your child in the eye can cause blunt trauma. Sharp penetrating trauma can be caused by a stick or projectile rock. Chemical trauma happens when the eye or the area around the eye is splashed with liquids like cleaning materials.
Permanent vision loss and blindness may be caused by eye injuries, so timely assessment and care are important. Nationally and globally, ophthalmologists at Riley at IU Health are known for specialist care of pediatric eye diseases and injuries.
Many eye injuries, caused by blunt trauma, are sports-related. That involves extreme injuries such as a fracture of an orbital blowout (a fractured bone under the eyeball), a broken globe (broken eyeball), or a detached retina. Bleeding within the eye (hyphema) can increase pressure because of blunt trauma and lead to permanent loss of vision.
When a child is injured by a ball or other blunt force or takes a fall with injury to the nose and cheekbone, bones near the eye may be broken. An eyeball may also be affected. Pain, redness, and tearing will result from scratching on the cornea. Sharp objects may cause the eye to have deeper lacerations that create a risk of permanent loss of vision.
An eyelid injury can vary from mild to severe. For instance, eye and eyelid swelling (a “black eye”) is typically a less severe injury, but the tear ducts or even the eyeball can be affected by an eyelid injury. The eyelid may also be damaged by a cut or laceration.
Eye and Eyelid Trauma/injury diagnosis
To assess eye injuries, various testing techniques are used. Depending on the type of injury, an X-ray or a computer tomography (CT) scan can be done to investigate eye damage. For some kinds of eye injuries, ultrasound can also be useful.
To expose a scratched cornea, ophthalmologists may put yellow dye (fluorescein) into the eye. If the surface of the eye is cut off by a deeper laceration, there is a chance of permanent vision loss.
Read Battery Acid on Skin
Treatment
Anytime your child has an eye injury, seek urgent medical attention. Although an injury can at first appear to be minor, a timely medical evaluation may mitigate further damage and avoid permanent loss of vision or blindness.
At IU Health, ophthalmologists at Riley will test vision function and closely inspect all the eye structures. After an eye injury, our doctors will also provide long-term treatment and follow-up that might be required.
If your child’s eye is splashed with a chemical, wash the eye with water immediately for about 15 minutes and go to an ophthalmologist or emergency room. If (like a fishhook) a sharp object penetrates the eye, do not remove it. Take the kid to the emergency department.
Treatment for an injury to an eye or eyelid depends on the form of injury. For various forms of eye injuries, below are a few guidelines and treatments:
- To avoid complications and preserve vision, deep lacerations to the eye require immediate treatment and sometimes surgery by an ophthalmologist.
- Your child may be prescribed antibiotic eye drops or ointments for a scratched cornea and/or wear a pressure patch on the eye.
- Prompt surgical care may be required for suspected broken bones near the eye to avoid long-term complications such as double vision, vision loss, and irregular appearance.
- If your child has an eyelid fracture, the full extent of the injury will be assessed by an ophthalmologist.
- An ophthalmologist should promptly assess trauma that causes swelling of the eyelid, red-eye, pain, or discharge.
With eye injuries, before the eye recovers, regular follow-up with an ophthalmologist may be required.
Takeaway
- The eyelids, the bones around the eye, or the eyeball may be affected by ocular trauma and eyelid trauma.
- Permanent vision loss and blindness may be caused by eye injuries, so timely assessment and care are important.
- Blunt trauma, sharp trauma, or chemical trauma may inflict injury.
- At first, eye injuries can appear to be minor, but immediate medical treatment is necessary to assess the injury, minimize further damage and avoid loss of vision.
- Until the eye recovers, regular follow-up with an ophthalmologist may be needed.
Last Updated on February 23, 2022 by Learn From Doctor Team