Table of Contents
Is Drowning Painful? Overview
Is drowning painful? The answer is “yes, drowning is quite painful.”. Drowning is a form of violent asphyxiation where the respiratory passage is occupied by fluid (e.g. water), due to submersion underwater & inhalation of water.
To know why drowning is painful you’ve to know the mechanism of drowning. We’ll discuss this along with other facts associated with drowning.
Types of drowning
Drowning is of four types;
1) Wet drowning:
- Fresh-water drowning.
- Sea-water drowning.
2) Dry drowning.
3) Secondary drowning (near-drowning).
4) Immersion syndrome.
The mechanism that makes drowning painful
Mechanism of drowning in a non-swimmer
Ignorance: Due to the ignorance of how to swim and due to panic and apprehension, the victim of drowning first swallows and inhales water
↓
Thus the air in the lungs is gradually replaced by water.
↓
These increase the weight of the body which ultimately submerges totally under the water surface.
↓
When the panicked victim cries for help
↓
A good amount of air comes out from the lungs
↓
In the attempt of inspiration
↓
When some water comes in contact with the laryngeal opening
↓
Automatic cough reflex
↓
Thus a part of the reserve air from the lungs also comes out
↓
Simultaneously, as the victim engulf some water, the weight of the body further increases
↓
Ultimately the mean specific gravity of the body becomes more than that of the water
↓
Final drowning
Cause of Painful Drowning
- For a swimmer: Exhaustion or other adversities.
- For a non-swimmer: Incapability to utilize the buoyancy of the body to keep the nose and mouth above the surface level of the water.
Pathophysiology of Painful Water Drowning
You may curious to know what happens inside your body in case of drowning in more details. To know that we’ll discuss that in two sections.
- Fresh Water Drowning(e.g. River, Pond, Lake, etc.)
- Sea Water Drowning(e.g. Sea)
Pathophysiology of Painful Fresh Water Drowning
When drowning occurs in fresh water and water enters the lungs
↓
Due to the difference in the osmolarity between the inhaled fresh water and the blood
↓
There is a passage of water from the lungs to the circulation
↓
As a result, the Chloride level in the blood of the left side chambers of the heart decreases to
almost its 50% value, there is haemodilution which ultimately causes hemolysis with resultant
absolute and relative low count of RBC and increase in the plasma K+ level.
↓
- Increased load on the heart due to increased volume of the blood.
- Heart muscle also suffers from hypoxia.
↓
Heart failure & ventricular arrhythmia (e.g. ventricular fibrillation)
↓
Death of the victim
Pathophysiology of Painful Sea Water Drowning
In saltwater drowning
↓
Water enters the lungs
↓
(High osmolarity of the inhaled water)
↓
Shifting of water from the blood is drawn in the lungs which causes
↓
- Pulmonary edema.
- Hemoconcentration.
- 30-40% increase in the level of Chloride in the blood of the left side chambers of the heart.
- Increased plasma volume.
- Increased Mg concentration.
- The relative increase in the RBC of the blood.
- (Microscopically) The crenated appearance of the RBC.
↓
Hypoxia(low level of oxygen in tissue)
↓
Death

Read Hyperpyrexia
Biochemical Changes in Painful Water Drowning
Biochemical Changes in Painful Freshwater Drowning
- Hemodilution
- Absolute & relative low count of Hb (Anaemia).
- Haemolysis → Hyperkalemia
- Hyponatremia
Biochemical Changes in Painful Seawater Drowning
- Hemoconcentration
- Increased RBC count.
- Shrinkage of RBC occurs.
- Hypermagnesemia
Absolute Medical Causes of Painful Water Drowning Death
In short Causes of Painful Water Drowning Death
- Asphyxia (inhalation of fluid causes obstruction of the air passage) →anoxia of both myocardium
- & the respiratory center ~ circulatory & respiratory failure.
- Ventricular tachycardia & fibrillation.
- Laryngeal spasm.
- Vagal inhibition.
- Exhaustion
- Injuries: Fracture of the skull, fracture-dislocation of cervical vertebra, etc.
Causes of Painful Water Drowning Death(In details)
1) In case of dry drowning
- Asphyxia due to laryngeal spasm.
- Vagal inhibition.
- Heart failure.
2) In case of wet drowning type-HA:
- Ventricular fibrillation.
- Circulatory volume overloads →heart failure.
- Hypoxia of heart muscle ~ heart failure.
3) In case of wet drowning type-JIB:
- Haemoconcentration.
- Pulmonary edema.
4) In case of immersion syndrome: Vagal inhibition.
5) In the case of divers: Head injury may also be the cause.
6) In case of seawater drowning: Gnawing by aquatic animals: e.g. shark fish may also the cause.
7) In all cases: Subsequent edema & infection may also the cause.
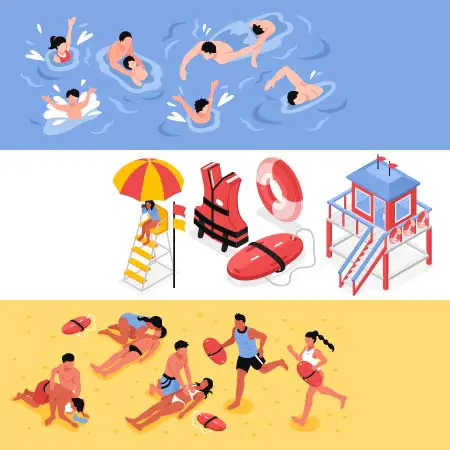
Prevention of Painful Drowning
Drowning can occur instantly, so being vigilant about drowning prevention is important.
Drowning is more common in kids between the ages of 5 and 14, and also some teenagers and adults over 65.
Children under the age of five are at an exceptionally high risk of drowning. Males, particularly teenage males, are at a greater risk than girls.

Some steps that you should follow to prevent drowning;
Pools and water entry points should be fenced off.
If you live by a lake or have a pool, putting up an access fence between the water and children who can’t swim unassisted can make the difference between life and death.
Make sure your children learn swimming
Lessons from a licensed, CPR-certified teacher will help children and adults overcome their fears of water while still instilling in them a healthy respect for how dangerous it can be.
In the case of water, always keep an eye on your kids.
Never leave children unattended while they are playing in the water, whether it is in the bathtub, shower, or even a small above-ground pool.
Drowning is the leading cause of accidental child mortality in the United States for children aged one to four.
Note that children will drown even though they are not in deep water. And in shallow water, it can happen.
Make sure you have some inflatable floating objects
If you’re going to a pool or lake, make sure there are floating items for people to hold onto if they fall into the water above their heads.
Inflatable life vests, puddle joggers, or “swimmies” should be worn by children who are not yet able to swim unassisted.
Avoid alcohol while you are in poor or water
Swimming and alcohol should not be combined. When swimming in a stream, river, or ocean, avoid being inebriated. Limit your alcohol intake, especially on hot days when you are more likely to be dehydrated than normal.
Learn how to do CPR.
Take a CPR course if you own a pool or a boat. You want to be secure in your ability to save someone who is drowning while you wait for emergency medical assistance.
Primary Treatment for Painful Drowning
Call 911 if you see someone is drowning
Seek assistance
- If a lifeguard is nearby, warn them. If not, have someone call 911 for you.
- If you’re on your own, follow the directions below.
Remove the individual from the water as soon as possible
Make sure that the victim is breathing or not.
- Place your ear near the mouth and nose of the individual. Is there any air on your cheek?
- Examine the person’s heart to see if it is beating.
Check the person’s pulse if they aren’t breathing.
- For 10 seconds, check the person’s pulse.
Begin CPR if there is the absence of a pulse.
- Place the person on the back with care.
- Place the heel of one hand on the middle of the chest at the nipple line for an adult or infant. Pushing with one hand on top of the other is also an option. Place two fingers on the breastbone of an infant.
- Press down at least 2 inches for an adult or infant. Make sure you don’t push too hard on the ribs. Press down about 1 1/2 inch for a baby. Be sure not to push on the breastbone’s end.
- Just perform chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute or higher. Allow the chest to fully rise between pushes.
Check to see if the person is breathing again.
It’s important to remember that these guidelines aren’t intended to replace CPR training. The American Red Cross, local hospitals, and other groups all give courses.
If the person is still not breathing, repeat the procedure.
- You will now open the airway by tilting the head back and raising the chin if you’ve been skilled in CPR.
- Close the victim’s nose with a squeeze. Take a natural breath, then cover the victim’s mouth with yours to make an airtight seal, then take two one-second breaths while keeping an eye on the chest for movement.
- Give 2 deep breaths, then 30 chest compressions.
- Continue this period of 30 compressions and 2 breaths before the individual regains consciousness or emergency assistance arrives.

Few Last Words
Drowning death is painful and mostly accidental. We should follow the prevention measure to prevent this painful drowning death. Since most victims of drowning are children we should take extra care of them. Thank you.
Read Breath smells like mothballs
Last Updated on February 23, 2022 by Learn From Doctor Team