Table of Contents
Overview
Sickle cell anemia is a hereditary disorder and can affect almost anybody, including white people. It’s caused by the production of hemoglobin-S (which is abnormal hemoglobin).
Sickle cell disease is caused by two genes that produce that abnormal hemoglobin-S. Hemoglobin is a protein molecule that carries oxygen in our bodies.
The red blood cell in the sickle cell trait people become the crescent shape and cannot carry enough oxygen. The crescent-shaped red blood cells cannot pass through small vessels and often cause a clot and interrupt the blood flow.
The clot of blood caused by sickle cell results in extreme pain and other medical complications.
Due to insufficient oxygen supply to the tissue, the person is unable to perform extreme physical activity, climbing a high mountain or such stuff.
In most instances, one gene is causing sickle cell disease; the person can live a normal life.
What is Sickle Cell Trait?
When a person carries a gene that can cause sickle cell disease, they have sickle cell traits.
Sickle cell trait isn’t a disease; people live a healthy life with it.
However, extreme exercise, dehydration, and a few other activities can cause some life-threatening conditions in a person with sickle cell trait.
A person with sickle cell trait can pass their genes to their children.
Which Blood Type Carries Sickle Cell?
Sickle cell trait is carried by the Red Blood Cells (erythrocytes). The red blood cells become crescent shape in the person with sickle cell trait and contain low hemoglobin.
Low hemoglobin content cannot carry enough oxygen to the tissues and therefore cannot match tissues demand.
What is Sickle Cell Disease?
Most of the people with sickle cell traits are asymptomatic. Some of the individuals can experience some blood and urine symptoms. The arisen symptoms because of sickle cell trait is known as sickle cell disease.
Some aggravating factors such as high altitude, extreme exercise, severe dehydration can cause the red cells of the blood to become sickled in the individual with sickle cell trait.
Sickle cell disease may lead to multiple complications that include;
- Reduce blood flow to the spleen leading to ischemia and necrosis
- Increased intravascular pressure into the eyes
- Muscle breakdown
Risk Factors of Sickle Cell
Sickle cell trait can affect almost anybody, but it is more likely to affect people of some common groups.
- African Americans
- Hispanics
- South Asians
- Caucasians (more specifically from southern Europe)
- People from middle east countries
Sickle cell traits are now tested in the USA and other countries during pregnancies and after birth. It helps pregnant mothers to make decisions about their babies.
Amniotic fluid and tissues of the placenta are used to detect sickle cell traits during pregnancy.
The African Americans are most affected by the sickle cell trait in the USA.
However, white people can get sickle cell, mostly the white people of southern Europe.
Acute Chest Syndrome Sickle Cell
Acute chest syndrome sickle cell is a complication of sickle cell disease. Despite it being an acute complication of sickle cell disease, it’s the primary cause of morbidity and mortality of sickle cell people.
Acute chest syndrome sickle cell shows varying radiological signs, fever, and respiratory symptoms.
Acute chest syndrome occurs mostly in children with sickle cell traits.
How Acute Chest Syndrome Occurs?
Acute chest syndrome sickle cell occurs when sickle cell clumps together in the pulmonary vessels within the lungs.
It occurs mostly in children and young adults with sickle cell traits.
The aggravating factors of acute chest syndrome include;
- Certain lung infections such as pneumonia, mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB), parasites, and helminths
- Existing pulmonary conditions (painful or painless)
- Post-surgical conditions
- Congenital lung anomalies
Acute chest syndrome can be life-threatening and should be treated on an emergency basis regardless of age.
Sickle Cell Acute Chest Syndrome Symptoms
- Chest pain
- Tightness of the chest
- High-grade fever ( more than 101 degrees F)
- High breathing rate
- Incomplete breath
- Cough
- Difficulty in breathing
Diagnosis of Acute Chest Syndrome
The diagnostic procedure of acute chest syndrome includes;
- Clinical diagnosis (physical signs and symptoms)
- X-rays
- Certain blood tests
Treatment of Acute Chest Syndrome
The treatment of acute chest syndrome sickle cell is conservative and effective. Therefore, the treatment should start right away after diagnosis.
- Antibiotic to eliminate lung infections
- Drugs to improve breathing
- Oxygen therapy if the oxygen saturation is low
- Bronchodilators
- Blood transfusion (Not necessarily needed)
Prevention of Acute Chest Syndrome
There is no specific prevention method for acute chest syndrome. However, following some prevention methods may help the person with sickle cell prevent it.
- Keep yourself active; try to take a walk every day. Jogging is a good option. Physical activity increases the blood flow through the pulmonary vessels and helps to prevent acute chest syndrome.
Caution: Avoid extreme workouts or physical activity.
- Take a long breathe sometimes. Practicing yoga is helpful in this case. Yoga teaches you to take long breathes and hold your breaths.
- Use a spirometer if the doctor suggests.
When to Seek Emergency Care?
Acute chest syndrome can be life-threatening if not treated immediately. If the patient with sickle cell trait experiences any symptoms, seek emergency care right away.
Meanwhile, take deep breaths to supply more oxygen to your lungs.
Sickle Cell Eyes ( Sickle Cell Retinopathy)
Sickle cell disease arises certain eye manifestations that can be divided into;
- Anterior eye disease: chamber of the eyes
- Posterior eye disease: It includes the retina, optic nerve, blood vessels, and subretinal tissues.
Signs and Symptoms of Sickle Cell Eyes
Sickle cell can affect the eyes and arise various manifestations. The signs and symptoms may include;
- Redness of eyes
- Hemorrhage (often subconjunctival)
- Atrophy of the iris
- Neurovascularization ( growth of new blood vessels on iris)
- Retinal hemorrhage
- Pigmentation
- Glistening deposits
- Blood vessels occlusions
Diagnosis of Sickle Cell Eyes
Diagnosis of sickle cell eyes includes clinical examinations and some laboratory investigations.
- Measuring intraocular pressure: measuring intraocular pressure is essential for interpreting eye conditions. Using an anesthetics drop a fine device is pressed into the eyes for a few seconds to read the intraocular pressure.
- Visualize new vessels: An atropine-containing drop is used that dilates the pupil and lets the doctor visualize the neurovascularization.
- Identifying hypoxic areas: Fluorescein angiography is used to see the areas of the retina that are not supplied by the vessels.
- Comprehensive eye examinations: Annual eye examinations should be performed for early recognition and prevention of sickle cell eye complications.
Treatment of Sickle Cell Retinopathy
Increased intraocular pressure may lead to serious eye complications, including blindness. Therefore, the treatment of sickle cell retinopathy should be started immediately.
The Conservative Treatment
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
- Hyperosmotic agents
- Adrenergic agonists (for treating glaucoma)
Alternatives: Beta-blockers and prostaglandin analogs
Surgical Treatment
- Retinal detachment
Sickle Cell Thalassemia
Thalassemia is an inherited disorder in which the body hemoglobin is lesser than normal, resulting in anemia.
A thalassemic patient needs a regular blood transfusion to survive in most cases.
Less hemoglobin content cannot carry enough oxygen to the tissues, and that may cause weakness, fatigue, and other medical complications.
A healthy diet, proper exercise, and yoga may help lead a normal life and blood transfusion.
Common Causes of Thalassemia
Thalassemia is caused by mutation of the DNA that makes hemoglobin. The mutated gene passes from parents to children, thus causing thalassemia.
There are two protein chains in hemoglobin: alpha and beta chains. Mutation in the alpha gene leads to alpha thalassemia, and mutation in the beta gene leads to beta-thalassemia.
Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Weightloss
- Pale skin
- Poor growth
- Dark or cloudy urine
Sickle Cell and Thalassemia
The drugs used to treat sickle cell increase hemoglobin production and may help relieve some symptoms of thalassemia.
Treatment of sickle cell and thalassemia should be continued together.
Sickle Cell Vaso-occlusive Crisis
In sickle cell disease, the red blood cells become crescent (sickle) shaped and contain less hemoglobin, thus carrying less amount of oxygen.
The crescent-shaped red blood cells cannot pass through small vessels and capillaries. They often occlude the vessel lumen and obstruct the blood flow; this phenomenon is known as sickle cell vaso-occlusive crisis.
Phases of Sickle Cell Vaso-Occlusive Crisis
The First Phase
This phase lasts around three days and is characterized by low-intensity pain and is often associated with numbness of the affected region.
The Second Phase
It is characterized by rapidly increasing pain, and the affected tissues die by loss of oxygen.
The Third Phase
This phase lasts several days and is accompanied by severe persistent pain, tissue necrosis, and fever.
The Fourth Phase
This phase includes the resolution of the occlusions.
The complication of sickle cell vaso-occlusive crisis
- Hypoxia
- Tissue damage
- Tissue dying
- Necrosis
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Numbness
- Sickle cell retinopathy
- Acute chest syndrome
Treatment of Sickle Cell Vaso-Occlusive Crisis
Sickle cell vaso-occlusive crisis is extremely painful and needs immediate treatment. Opioid analgesics are often used to relieve pain.
Oxygen therapy vasodilators can be used. However, blood transfusion is necessary if the anemia persists.
Sickle Cell Life Expectancy
The average sickle cell life expectancy is about 42-47 years.
The life expectancy of people with sickle cell trait or disease depends on certain conditions such as;
- The severity of the complications
- Age of the person
- Acute chest syndrome
- Exercising and physical work habits
- Diet
Despite the person having an average life expectancy of 42 to 47 years, people without complications may live much longer and lead a normal life.
Severe complications such as sickle cell acute chest syndrome should be treated immediately. Otherwise, it can be life-threatening.
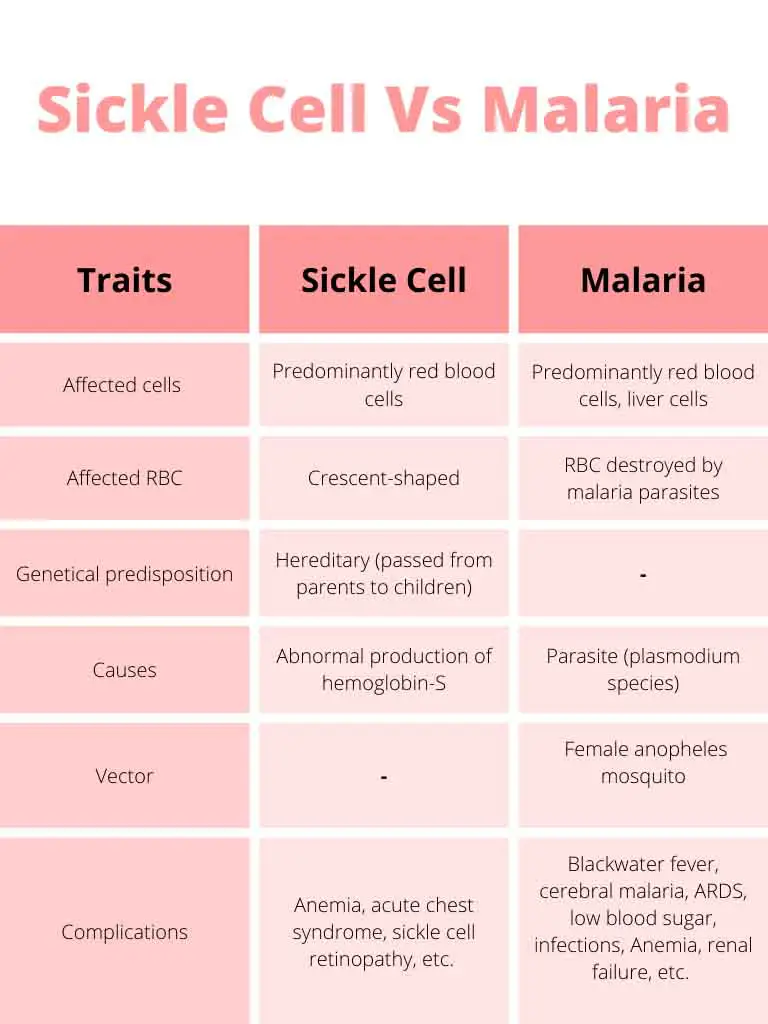
Compare Sickle Cell Disease and Malaria
The sickle cell disease and malaria parasites both affect the red blood cells. There are some similarities and differences between these two conditions.
|
Traits |
Sickle Cell Disease |
Malaria |
|
Affected cells |
Predominantly red blood cells |
Predominantly red blood cells, liver cells |
|
Affected RBC |
Crescent-shaped |
RBC destroyed by malaria parasites |
|
Genetical predisposition |
Hereditary (passed from parents to children) |
– |
|
Causes |
Abnormal production of hemoglobin-S |
Parasite (plasmodium species) |
|
Vector |
– |
Female anopheles mosquito |
|
Complications |
Anemia, acute chest syndrome, sickle cell retinopathy, etc. |
Blackwater fever, cerebral malaria, ARDS, low blood sugar, infections, Anemia, renal failure, etc. |
Takeaway
Sickle cell disease passes from parents to children via the transfer of affected genes. It can be both asymptomatic and symptomatic.
The life expectancy of this disease is high, and in most cases, the person can lead a normal life.
Some complications of sickle cell disease can be life-threatening, such as acute chest syndrome.
Sickle cell disease mostly occurs in African American people. White people can get sickle cell disease.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is sickle cell contagious?
Sickle cell trait is a hereditary disorder that passes from parents to children. It’s not contagious, nobody around the affected person gets affected.
Can you die from the sickle cell?
Sickle cell trait is not dangerous unless it causes some life-threatening complications.
Acute chest syndrome in children, a vaso-occlusive crisis can lead to death if they are not treated properly.
However, the life expectancy of a person who has sickle cell is near the normal person.
How is the sickle cell allele maintained through natural selection?
Sickle cell trait is an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. It’s not related to x linked disease. The sickle-cell allele is maintained through autosomal recessive inheritance.
Last Updated on February 14, 2022 by Learn From Doctor Team